|
| Adrenal Function Urine Test |
| Sulkowitch Urine (Calcium) Test |
|
|
|
CADMIUM
Number 48 on the "periodic table" of elements
Tests the presence of ions of Cadmium to a high degree of accuracy to
detect contamination in the body and on a wide range of materials in your environment
Cadmium levels in humans tend to increase with age, usually peaking at around age 50 and then levelling off.
No cadmium is present in newborns. Interestingly, cadmium does not cross the placenta-fetal barrier nor the
blood-brain barrier as lead and mercury do, so it is not toxic to fetuses, nor does it cause the mental and
brain symptoms of lead and mercury
Cadmium is not very well absorbed, with a rate of about 20 percent, but this is still a higher rate than that
of other minerals. Cadmium is not particularly well eliminated by the body, mainly through feces and urine.
This mineral is stored primarily in the liver and kidneys. Cadmium like zinc is also stored in
the testes in higher concentrations than in other tissues. Cadmium accumulation in the kidneys (with aging)
may cause hypertension.
Sources
There are many sources by which our bodies can be contaminated with cadmium. Cigarette smoke, refined foods, water pipes, coffee and tea,
coal burning, and shellfish are all definite sources. Cadmium is also a component of alloys, used in electrical materials, and is present in
ceramics, dental materials, and storage batteries.
During the growth of grains such as wheat and rice, cadmium (from the soil) is concentrated in the core of the kernel, Refined flours, rice,
and sugar all have relatively higher levels of cadmium.
One pack of cigarettes contains about 20 mcg. of cadmium, or about 1 mcg. per cigarette. About 30 percent of that goes into the lungs and is
absorbed while the remaining 70 percent goes into the atmosphere contaminating the environment. With long-term smoking, the risk of cadmium
toxicity is increased. Marijuana may also contain concentrates of cadmium, so regular smoking of cannabis may also be a risk factor for
toxicity from this metal.
Water pipes may be another source of cadmium contamination. Cadmium is often used to protect metals from corrosion. Soft or acid water is
corrosive and causes the metals in the pipes to break down, releasing cadmium and other minerals from them. Hard water containing calcium
and magnesium salts actually coats the pipes and protects against this leaching of minerals.
Other air pollution of cadmium comes from zinc mining and refining, and from the burning of coal. Cadmium is also an industrial contaminant
from the steel-making process.
Soil levels of cadmium are increased by cadmium in water, by sewage contamination, by cadmium in the air, and by high-phosphate fertilizers.
Coffee and tea may contain significant cadmium levels. Root vegetables such as potatoes may pick up cadmium, and the grains can concentrate
cadmium. Seafood, particularly crustaceans, such as crab and lobster, and mollusks, such as clams and oysters, have higher cadmium levels.
Toxicity
Cadmium has no known useful biological functions. Cadmium competes with zinc for binding sites and can therefore interfere with some of
zinc's essential functions. In this way, it may inhibit enzyme reactions and utilization of nutrients. Cadmium may be a catalyst to oxidation
reactions, which can generate excessive free-radical activity leading tissue damage and health issues.
Toxicity Limits
The exact levels where organic cadmium becomes toxic is not clear. About 40-45 mcg. intake daily is probably safe. Below 0.015 - 2 ppm is
considered current normal ranges. The reading for inorganic cadmium presence should be 0.
Check out cadmium levels in your body with our easy to use, home-based, HMT Cadmium Test kit
 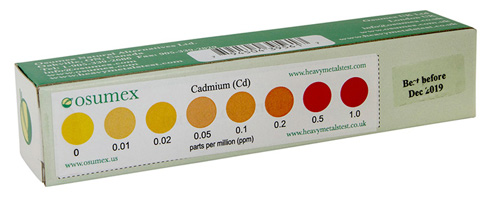
Sample of a HMT Cadmium Test kit
Osumex HM-Chelat is most effective in eliminating heavy metals contamination in the body

The above information is provided for general
educational purposes only. It is not intended to replace competent
health care advice received from a knowledgeable healthcare professional.
You are urged to seek healthcare advice for the treatment of any
illness or disease.
Health Canada and the FDA (USA) have not evaluated these
statements. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent
any disease.
|


